The technologies of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have the potential to fundamentally alter the world in which we live. However, they are now having trouble winning over customers’ and companies’ hearts and minds. What then, does the future really hold?

Virtual Reality
The use of computer technology to create a simulated environment is known as virtual reality (VR).
The head-mounted display (HMD) is the element of virtual reality that is most easily recognized. Because humans are visual creatures, the most significant distinction between immersive Virtual Reality systems and conventional user interfaces is frequently the display technology.
The three primary types of VR
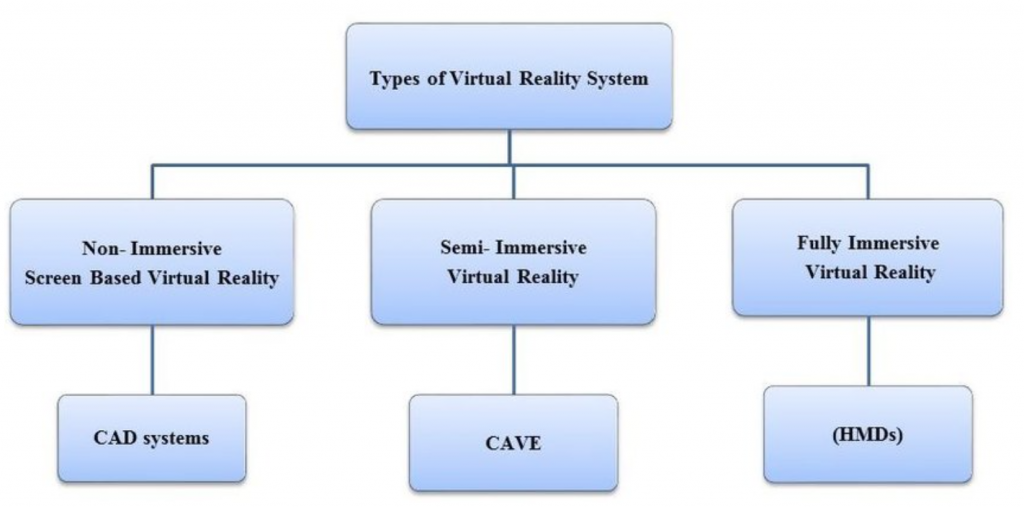
1. Non-immersive VR: Virtual reality that isn’t immersive is frequently disregarded because it’s so widespread. This technology creates a virtual world on a computer, but the user is still aware of and in control of their physical surroundings. A good example of non-immersive VR is video gaming.
2. Semi-immersive VR: This kind of VR offers an experience that is partially based in a virtual setting. When combined with graphics computing and big projector systems, such as flight simulators for aspiring pilots, this kind of VR makes sense for instruction and training.
3. Fully Immersive VR: At the moment, fully immersive VR technologies are not yet available. However, because of how quickly technology is developing, they might be. With this kind of VR, the simulation experiences are the most lifelike in terms of sight, sound, and occasionally even smell. Games that simulate racing in a car are an example of immersive virtual reality since they give the player a sense of speed and dexterity. VR is increasingly being used in fields outside of entertainment and games.
Augmented Reality
The real-time integration of digital information with the environment of the user is known as augmented reality (AR). Users of augmented reality (AR) encounter a real-world environment with created perceptual information superimposed on top of it, as opposed to virtual reality (VR), which produces a completely artificial environment.
Using augmented reality, users can receive more information or have natural environments aesthetically altered in some way. The main advantage of augmented reality (AR) is that it successfully combines digital and three-dimensional (3D) elements with how people perceive the real world. AR has several applications, from entertainment to aiding in decision-making.
Virtual Reality (VR) vs. Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual reality (VR) is a completely comprehensive, all-encompassing artificial experience that hides the real world. Augmented reality (AR) uses digital overlays that combine synthetic items to improve users’ perceptions of their surroundings.
VR produces artificial environments by using sensory input. Users’ actions influence the environment created by the computer, at least in part. In contrast to the actual world as it exists today, digital surroundings mirror genuine places.
In augmented reality, the real world is seen directly or through a device like a camera to create a visual, and computer-generated inputs like still images, music, or video are added to that vision. Because AR enhances the real-world experience rather than producing a brand-new one, it differs from VR.
AR and VR: Not a competition but are complimentary
Significant differences exist between AR and VR. But this obvious distinction does not imply that one of the two technologies is superior to the other. Rather, both technologies excel in distinct application domains:
- AR enhances a real-world scene, while VR provides an immersive virtual experience.
- While just 25% of AR is virtual, VR is 75% virtual.
- Unlike AR, VR requires a headgear device.
- While AR users interact with the real world, VR users navigate through a wholly made-up environment.
- Compared to VR, AR demands more bandwidth.
- AR aims to improve both the actual world and the virtual one. Virtual reality (VR) replaces the real environment with a made-up reality that is largely used to improve video games.
A symbiotic relationship of superior systems is created when AR and VR are used together. Even while they can function independently, together they provide users with a better and more interesting experience. The idea behind this is to construct a realm of fiction that permits communication with the real world. At the end of the day, it does not matter which technology will dominate our future, we must find a way to combine and take advantage of both AR and VR to build more realistic solutions in various industries.
Read more to get insights on Big Data, GraphQL and other interesting tech stuff.